Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) is a managed SQL database service provided by Amazon Web Services. Amazon RDS is easier to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud. It provides cost-efficient, resizable capacity for an industry-standard relational database and manages common database administration tasks.
- Mon-Sat 8.00 - 20.00
- (+84) 976-099-099
Amazon RDS
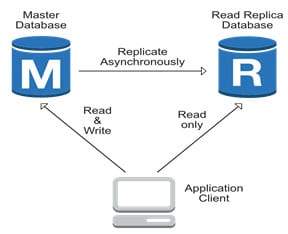
Amazon RDS Read Replicas
Amazon RDS Read Replicas provide enhanced performance and durability for database (DB) instances. This feature makes it easy to elastically scale out beyond the capacity constraints of a single DB instance for read-heavy database workloads. Read replicas can also be promoted when needed to become standalone DB instances.
AWS Services
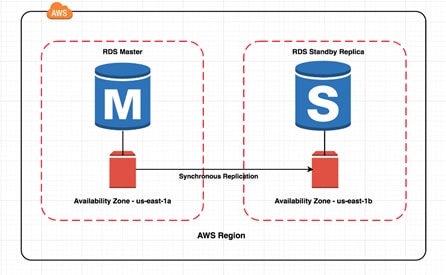
High Availability and Disaster Recovery (HA &DR)
Amazon RDS Multi-AZ (Availability Zone) deployments provide enhanced availability and durability for Database (DB) Instances. When you provision a Multi-AZ DB Instance, Amazon RDS automatically creates a primary DB Instance and synchronously replicates the data to a standby instance in a different AZ. Each AZ runs on its own physically distinct, independent infrastructure, and is engineered to be highly reliable. In case of an infrastructure failure, Amazon RDS performs an automatic failover to the standby, so that you can resume database operations as soon as the failover is complete.
RDS Features and Benefits
DS is designed to reduce operational costs and overcome some common challenges that businesses experience when running databases through tools like MySQL. Its primary benefits include:
- Precise, independent scaling: A hardware-based solution can cause inefficiencies in database management because resources (CPU, memory, storage, etc.) come bundled together. RDS allows developers to easily change these factors independently so they can fit them to the needs of their databases.
- Ease of implementation: Because RDS integrates with common database applications, developers can continue working in the programs with which they are already familiar.
- Process automation: Database backups, software patching, failure detection, and recovery are all a part of ongoing database management that can lead to significant costs. Amazon RDS automates these to reduce the administrative burdens.
- Security: Amazon RDS restricts access to database instances, where advanced privileges are required, and prevents shell access. Its integration with AWS makes it possible to manage databases in the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)and expand security features with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
- Reliability and availability: Amazon RDS include replication that allows for high availability on high-priority databases and automatic failover if a primary database becomes unavailable.
- Cost: Amazon’s pricing options for RDS include on-demand and hourly rates, adapted to the actual resource demands of database applications.
- Faster deployment: RDS overcomes the need for provisioning and investment in hardware resources, speeding up the time from conception to deployment.
Amazon RDS database engines
An AWS user can spin up six types of database engines within Amazon RDS:






Subscribe
Get the latest tips, software updates and promos.
